
Homework #7
 |
CS 107 - Introduction to Scientific Computation Homework #7 |
1. RNA Transcription: DNA and RNA consist of sequences of nucleotides.
DNA nucleotides each contains one of the following bases: adenine, cytosine,
guanine, and thymine, abbreviated A, C, G, and T, respectively. In
bioinformatics, a DNA sequence is often represented as a string made up of these
abbreviated base names (e.g. "GATTACA"). RNA uses uracil (U) in place of
thymine (T). When RNA is transcribed from DNA, the result is a "copy" of
the DNA sequence with uracil (U) substituted in the RNA for each occurrence of
thymine (T) in the DNA. Create a function transcribe.m that takes a string
of DNA bases, and returns the corresponding string of transcribed RNA bases.
For example:
>> transcribe('GATTACA')
ans =
GAUUACA
2. RNA Codon Translation: Exercise 8.7. Create a function
rna2amino that takes two arguments, an RNA nucleotide sequence
string and a starting index, and returns the amino acid sequence string that
would be translated.
Hint: One approach makes use of a switch/case statement to map sets of codons to the smaller number of acids/'Stop'. Another approach would be to start your definition as follows:
function res = rna2amino(bases, startIndex)
acids = ['Phe'; 'Ser'; 'Tyr'; 'Cys'; ...
'Phe'; 'Ser'; 'Tyr'; 'Cys'; ...
'Leu'; 'Ser'; 'Stp'; 'Stp'; ...
'Leu'; 'Ser'; 'Stp'; 'Trp'; ...
'Leu'; 'Pro'; 'His'; 'Arg'; ...
'Leu'; 'Pro'; 'His'; 'Arg'; ...
'Leu'; 'Pro'; 'Gln'; 'Arg'; ...
'Leu'; 'Pro'; 'Gln'; 'Arg'; ...
'Ile'; 'Thr'; 'Asn'; 'Ser'; ...
'Ile'; 'Thr'; 'Asn'; 'Ser'; ...
'Ile'; 'Thr'; 'Lys'; 'Arg'; ...
'Met'; 'Thr'; 'Lys'; 'Arg'; ...
'Val'; 'Ala'; 'Asp'; 'Gly'; ...
'Val'; 'Ala'; 'Asp'; 'Gly'; ...
'Val'; 'Ala'; 'Glu'; 'Gly'; ...
'Val'; 'Ala'; 'Glu'; 'Gly'];This is a 64x3 character array that has
the take amino acid entries left-to-right, top-to-bottom. Suppose you used
strfind('UCAG', base) - 1, to assign an individual base a number (e.g.
strfind('UCAG', 'A') - 1 → 2).
Consider, for a given codon, how the change of a single base's number in a
single position (holding all others fixed) affects the index of the desired
acid. Form a mathematical expression from the codon's three base numbers
to the acid (converting a 'Stp' result to 'Stop').3. Dot Plot: A dot plot is a means of visually comparing similarity of two base sequences. Given two strings s1 and s2 of bases, coordinate (i, j) of the plot is black if s1(i) == s2(j), and is white otherwise. NOTE: Strings s1 and s2 may have different lengths. We'll accomplish this by building a 2D array (i.e. a matrix) x of 0's and 1's, corresponding to mismatches and matches, respectively. We plot them as follows:
colormap(gray(2)); image(2 - x); axis ij; axis square;
For example,
dotPlot('gattaca','gattaca')
yields
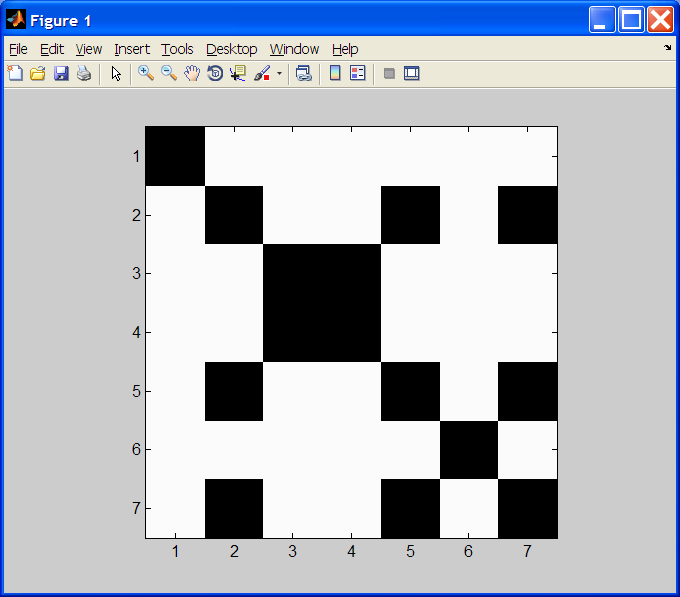
Create function
dotPlot that takes two base sequence strings, computes the dotplot
data matrix, plots it as above, and returns the dotplot matrix.